AC MACHINES-1 (66761) Theory
10. Realize the principle and construction of 3-phase induction motor.
10.5. Describe the construction of stator of an induction motor.


Construction of 3 Phase Induction Motor
The main body of the Induction Motor comprises of two major parts:
Stator
The stator is made up of a number of stampings in which different slots are cut to receive 3 phase winding circuit which is connected to 3 phase AC supply.
The windings are wound for a definite number of poles depending upon the speed requirement, as speed is inversely proportional to the number of poles, given by the formula:
Ns= 120f/p
Where Ns= synchronous speed
f = Frequency
p = no. of poles
Induction motors work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Electrical energy from the stator winding is transferred to the rotor winding by electromagnetic induction. Therefore these are called as induction motors.Constructional Features of a Three Phase Induction Motor
A 3-phase induction motor consists of two main parts namely stator and rotor

Stator
It is the outer body of the motor and consists of outer frame, stator core and windings.
Outer frame
The outer frame acts as housing for the motor and supports the stator core. It also protects the inner parts of the motor. Fins are provided on the outer surface of the frame for heat dissipation and cooling of the motor. Frame is provided with legs/base plate to bolt it on the foundation. Motor housing is the outer cover or frame of the motor which contains stator, rotor and other parts. Fins are provided on the outer frame to increase heat dissipation. Housing can be square ( Fig.)
or round (Fig.)


Depending on the application it can made of any one of the following material:
a. Aluminum/ Aluminum alloy
b. Mild Steel
c. Stainless Steel
Stator core
It is made of high grade silicon steel stampings of thickness 0.3 to 0.6 mm which are insulated from each other by a varnish layer. To minimize the hysteresis and eddy current losses core is constructed of steel stampings of high magnetic permeability. The stampings are assembled one over the other under hydraulic pressure and are fixed into the frame. The function of stator core is to carry the alternating magnetic field. Slots are cut on the inner side of the stamping, as shown in fig. 17.9, to accommodate stator winding.
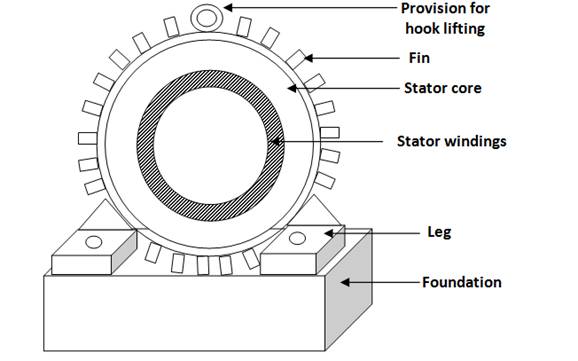
fig. Outer frame

fig. Stator Stamping
Stator winding
Coils of insulated wires are inserted into the slots of the stator. Each grouping of coils, together with the core it surrounds, forms an electromagnet (a pair of poles) on the application of AC supply. The number of poles of an AC induction motor depends on the internal connection of the stator windings. The three phase stator windings are connected directly to the three phase power source. Internally they are connected in such a way, that on applying AC supply, a rotating magnetic field is created. There are six terminals of the stator winding; two for each phase are connected in the terminal box of the motor. Number of poles depends on the speed requirement. For lower speed more number of poles are required as,
![]()
![]()