DATA COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
10. Understand Network Interface Cards (NIC) (chapter 10)
10.1 State the role of NIC.
10.2 Describe the format of Physical address (MAC Address) of NIC.
10.3 Mention the points that agree both the sending and receiving NICs.
10.4 State the importance of base memory address for NIC.
10.5 Mention the important points to maintain the compatibility among NIC, bus and cables.
10.6 Describe the NIC related factors that enhanced the performance of network.
10.1 State the role of NIC.
Before introducing the NIC definition, it's necessary to know there are quite a few names for the network interface card based on habits in different regions, such as network interface controller, Ethernet card, LAN card, network adapter or network adapter card (NAC). It seems a little bit confusing, but no matter what names the NIC has, they all refer to the circuit board that enables devices like computers and network servers to be connected over a network. Currently, the NIC card designed as a built-in style is commonly found in most computers and some network servers. Besides, network cards like server network card can also be inserted into expansion slots of devices.
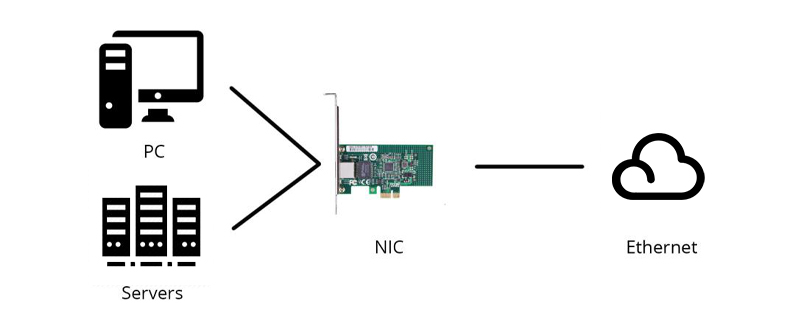
NIC definition is very simple, but what does a network interface card do and what is the function of NIC? Working as an interface at the TCP/IP layer, a NIC card can transmit signals at the physical layer and deliver data packets at the network layer. No matter what layer the network interface controller lies, it acts as a middleman between a computer/server and a data network. When a user requests a web page, the LAN card gets data from the user device, and sends them to the server on the internet, then receives the required data back from the Internet to display for users.Function of NIC
10.2
Describe the format of Physical address (MAC Address) of NIC.
What is a MAC address?
A MAC (Media Access Control) address is the hardware address of the Network Interface Card (NIC) of your computer. You must have it on hand to register for the UCInet Mobile Access network and campus-wide DHCP services. This Web page will help you locate and identify it so you may register your Network Interface Card (or cards) for the network.
Media Access Control (MAC) Addressing
The MAC address is the unique serial number burned into each network adapter that differentiates the network card from all others, just as your house number is unique on your street and identifies your home from all others. To be a part of any network, you must have an address so that others can reach you. Two types of addresses are found in a network: the logical (OSI model Layer 3, network) and the physical (OSI model Layer 2, data link). For this discussion of LAN environments, the physical address (also known as the Media Access Control [MAC] address) is relevant.
A MAC address is the physical address of the device. It is 48 bits (6 bytes) long and is made up of two parts: the organizational unique identifier (OUI) and the vendor-assigned address, as illustrated in Figure 5.1.
Figure 5-1. MAC Address

The MAC address on a computer might look like this: 00-08-a1-08-c8-13. This MAC address is used for the Fast Ethernet adapter on the computer in question. The OUI is 00-08-a1, and the vendor-assigned number is 08-c8-13.
The OUI is administered by the IEEE and identifies the vendor of the network adapter. The vendor-assigned portion of the MAC address is just that, the alphanumeric identifier assigned by the vendor. It is the combination of the OUI and the vendor-assigned number that ensures that no two network adapters have the same MAC address.
Finding Your MAC Address
Windows (two methods)
Method 1:
- Click Start and in the Search Programs and Files box type ncpa.cpl and then push Enter on your keyboard.
- The Network Connections window will appear. Double-click on either Local Area Connection icon (if you are trying to register your Ethernet/wired connection) or Wireless Network Connection.
- In the window that appears, click Details… and in the subsequent window you’ll see the Physical Address field: that is your MAC address.
Method 2:
- Click Start then Run (in Windows 7, Start and type in the Search Programs and Files box.)
- Enter: cmd
- Enter: ipconfig /all
If the output scrolls off your screen, and it will on Vista and Windows 7, use: ipconfig /all | more - The Physical Address is your MAC address; it will look like 00-15-E9-2B-99-3C. You will have a physical address for each network connection that you have.
