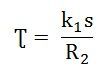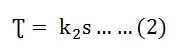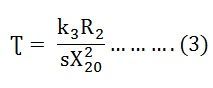AC MACHINES-1 (66761) Theory
11. Recognize the concept of development of rotating magnetic field and torque in rotor.
11.9. Draw the torque speed curve.
Torque Speed Characteristic of an Induction MotorTorque Speed Characteristic is the curve plotted between the torque and the speed of the induction motor. As we have already discussed the torque of the induction motor in the topic Torque Equation of an Induction motor.The equation of the torque is given as shown below.
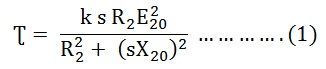
At the maximum torque, the speed of the rotor is expressed by the equation shown below.
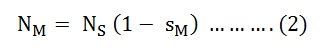
The curve below shows the Torque Speed Characteristic.
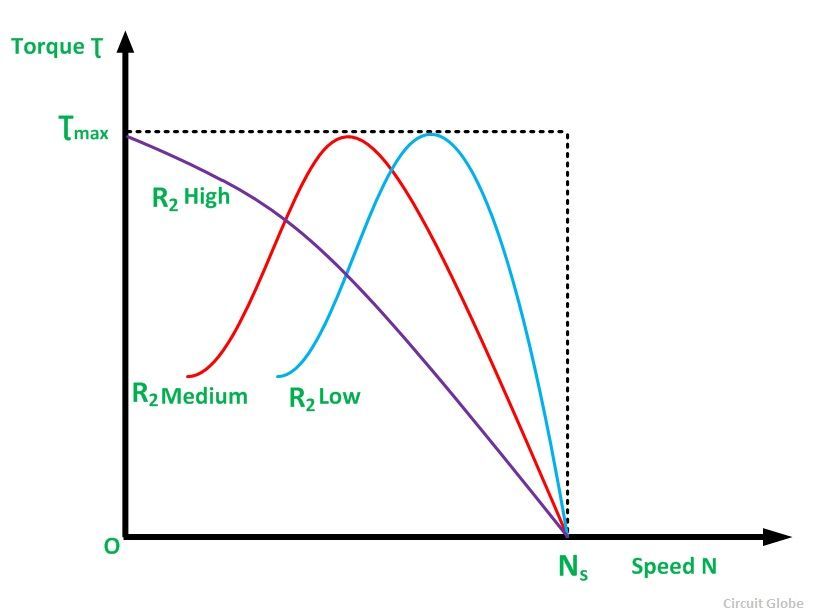
The maximum torque is independent of the rotor resistance. But the exact location of the maximum torque Ʈmax is dependent on it. Greater, the value of the R2, the greater is the value of the slip at which maximum torque occurs. As the rotor resistance increases, the pullout speed of the motor decreases. In this condition, the maximum torque remains constant.
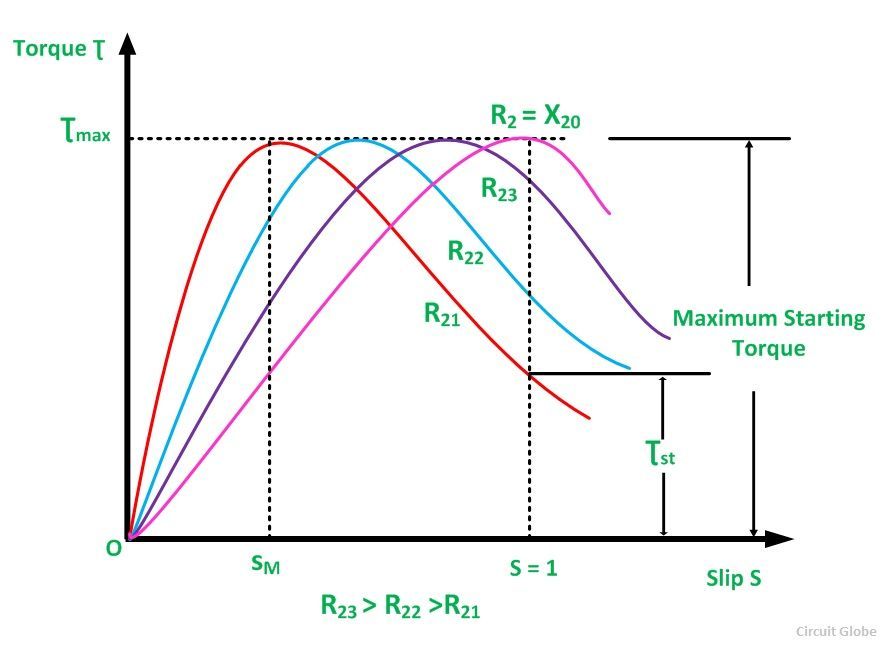
The Torque Slip Characteristic is represented by a rectangular hyperbola. For the immediate value of the slip, the graph changes from one form to the other. Thus, it passes through the point of maximum torque when R2 = sX20. The maximum torque developed in an induction motor is called the Pull Out Torque or the Breakdown Torque. This torque is a measure of the short time overloading capability of the motor. The torque slip characteristic curve is divided roughly into three regions. They are given below. The torque equation of the induction motor is given below. At the synchronous speed, s = 0, therefore, the torque is zero. When the speed is very near to synchronous speed. The slip is very low and (sX20)2 is negligible in comparison with R2. Therefore, If R2 is constant, the torque becomes When k2 = k1/R2 From the equation (1) shown above, it is clear that the torque is proportional to slip. Hence, in the normal working region of the motor, the value of the slip is small. The torque slip curve is a straight line. As the slip increases, the speed of the motor decreases with the increase in load. The term (sX20)2 becomes large. The term R22 may be neglected in comparison with the term (sX20)2 and the torque equation becomes as shown below. At the standstill condition, the torque is inversely proportional to the slip. Beyond the maximum torque point, the value of torque starts decreasing. As a result, the motor slows down and stops. At this stage, the overload protection must immediately disconnect the motor from the supply to prevent damage due to overheating of the motor. The motor operates for the values of the slip between s = 0 and s = sM. Where, sM is the value of the slip corresponding to the maximum torque. For a typical induction motor, the pull-out torque is 2 to 3 times the rated full load torque. The starting torque is about 1.5 times the rated full load torque.Related Terms:
Torque Slip Characteristic of an Induction Motor
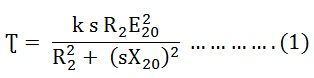
Low Slip Region
Medium Slip Region
High Slip Region
Related Terms: